Managing database backups on shared database instances without maintenance plan wizard.
Download Code
Problem
As the number of databases with different recovery models at different schedules exists in shared database instances, so do the challenges related managing the databases backups. Brent clearly described in his post about the few of the challenges http://www.brentozar.com/archive/2012/12/backups-gone-bad-the-danger-of-differentials/
Maintenance plans are very helpful to create and schedule the backups, but it has very limited features where you can’t control the backups of all the databases in shared database instances.
| | Maintenance Plans | This Solution |
| To Include the databases to the existing Plan | manual | dynamic query as a parameter "select name from sys.databases where name in ('db_1','db_2') |
| Copying/Moving the backups to secondary location | | supports.
set the job parameter "I_Optional_RemoteBkpPath]" with the secondary location path |
| Track the status (backup,copies,deleted) of each backup including its secondary locations | | supports.
select * from BKPS_DB_AUTO_LOG |
| delete the old backups based on dependencies instead age | based on age | based on your own query. |
| restart the job from the point of failure | | supports |
| dashboard monitoring | | supports.
create your own dashboard using the bkps_db_auto_log table. |
Below framework/solution addresses all the problems listed above. You can modify the same solution as per your requirement to control multiple instances with multiple databases. and you can configure and check whether the backup jobs are configured as per your DRP requirements.
- Backups all the databases based on the recovery model. by default it takes full database backups of all the databases and takes t-log backups only if the recovery model is full or bulk-logged.
- no manual intervention required to include the databases to take full backups
- track and moves the backup files from local server to secondary locations . once all the backups are completed in a batch.
- deletes the old backup files in sequence (full + dependent differential and t-log backups) instead based on the no.of days old at the secondary location.
- a daily report to ensure that all the backups are in place
Solution

Description :
Steps are very self descriptive.
- Get DB List : gets the list of the databases from the output of the input variable I_SqlDBList to include in local variable "dblist".
- Get Next Execution ID : insert a record in dbo.BKPS_DB_AUTO_LOG with an auto increment number during each execution
- Loop All DB List : loops through all the databases in the list
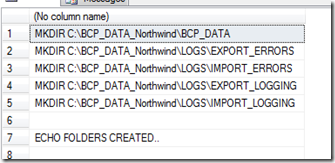
- creates a directory for each database in the local folder
- backup the database
- get files to move from local to remote location : If the optional variable @I_Optional_RemoteBkpPath is not null , then it assigns the list of the files to move to a local variable " moveFileList"
- Move and delete old files : loops through the list of the backup files assigned in step 1
- moves one file at a time in a loop
- get old file list to delete : get the list of the OLD files which are depends on the file which is just moved
- Loop old backups : loops through one file at a time to delete
- delete old backups : delete and log the status of the file deletion in the log table
Input variables Description
set the variables where name starts with I_ , rest are local variables

| Variable Name | Description |
| I_BkpExtension | Backup extension. Don’t enter “.” |
| I_BkpIsCompressed | Enter 1 to compress the backups |
| I_BkpIsVerify | Enter 1 to verify the backup |
| I_BkpType | Enter the backup type Full /Diff/Log |
| I_LocalBkpPath | Enter local database backup path. If you want to take the backups directly to a remote location then enter the remote location name |
| I_Optional_RemoteBkpPath | This is optional. Enter remote location to move the local backups to this location. |
| I_Optional_SqlRetention | This is Optional. Enter the select query to include the list of the backup files to delete. Eg: below query produce the list of old backups except recent,full +recent differential + all log backups after recent diff backup. select files_to_delete from vw_keep_recent_full_nd_diff |
| I_SqlDBList | Enter the select query to list the databases to take the backup. Eg: below value includes the backups X,Y,Z select name as dblist from master.sys.databases where name in ('X','Y','Z') You can filter the database based on your own criteria.
For e.g.: To take the log backups of all databases which are in full recovery model , set the variable value with “select name as dblist from sys.databases where recovery_model_desc='full' “ |
SSIS Flow Steps Description
Database Objects
- BKPS_DB_AUTO_LOG (Table) : it’s a tracking table , to store the status of the backup executions and location of the backup files
- fn_split_files : user defined function
- BKP_INS_BKP_STATS(procedure) : to insert the status of the backup operation in tracking table
- BKP_DBS_MULTI (procedure) : to take the backups
- vw_keep_recent_full_nd_diff(view) : this view contains the all the old files to delete from the remote location. You can change this view as per your retention plan.
Steps to configure the job on your lab server
1. Download all the files
2. Save the BKPS_DB_AUTO.dtsx as an external file in c drive
3. execute all the scripts (1-6) in MSDB database
Note: you should review and modify the view vw_keep_recent_full_nd_diff to delete the old backups , I have provided this view for simulation purpose only .
4. Create and Configure SQL Server agent Job
after executing the script "6.create Job BKP_DBS_AUTO" , it create a job with name "BKP_DBS_AUTO"
f you already has a job with the same name then modify the first line in the script with a new name for the job
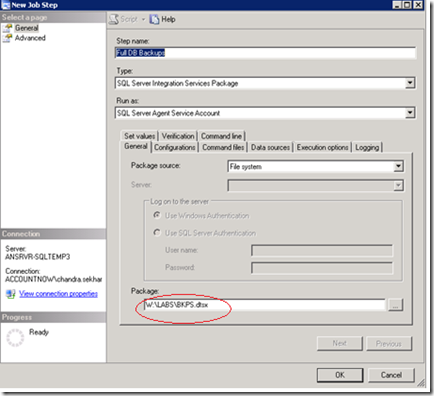
Go to SQL server agent , right click on “"BKP_DBS_AUTO" ” job , open the first step and modify the location of the SSIS package
1.
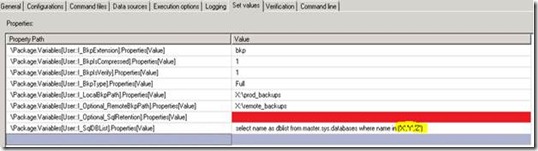
2 Click on [Set value] tab on same screen and modify the values for all variables as below example. Refer the section “variable description” in this article for the description of these variables

2. Execute the job, after successful completion of the job , you will see the records in msdb.dbo.BKPS_DB_AUTO_LOG table
3. Execute the job several times , and check the status column in the same table. it deletes all the old backup files and keep only the recent one. If you don’t want to delete the old backups then don’t pass any value to the variable I_Optional_SqlRetention
Next:
To create multiple jobs , you can script out the existing job and change the variable values
More on deleting old backups:
Attached download files has a view “vw_keep_recent_full_nd_diff” , this view refers the tracking table “bkp_file_locations” and produce the list of the remote old backup files to delete except the recent full ,recent differentials and all log files after the recent differential backup.
I have created a view to produce the list of the old backup files to delete to reuse it.
| create view vw_keep_recent_full_nd_diff as --select BFL.DBNAME,BFL.IID ,RECENT.IID ,BFL.BKP_TYPE ,RECENT.BKP_TYPE select BFL.BKP_REMOTE_PATH from BKP_file_locations BFL LEFT outer join (select MAX(IID)AS IID,DBNAME,BKP_TYPE from bkp_file_locations where bkp_type <> 'LOG' GROUP BY DBNAME,BKP_TYPE ) recent on recent.dbname = BFL.dbname AND recent.BKP_TYPE = BFL.BKP_TYPE AND recent.IID = BFL.IID WHERE RECENT.IID IS NULL AND BFL.status = 'moved' |
To test what database file are deleted. Run the below query, check the difference in status columns.
| select iid,DBNAME,bkp_type,status from BKP_file_locations order by dbname |
Below is the output for the databases X and Y