Changing Tracking: May not be a viable solution on OLTP databases.
As per Books Online: It tracks what rows are changed. The latest data can be obtained directly from the table that is being tracked. It’s a light weight method to track the changes, unlike triggers which needs programming with additional tables and cleanup process."
Create database TestDB
Go
Use TestDB
Go
|
USE TestDB
GO
create table [Customer](
IID INT IDENTITY (1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED,
[CustomerID] [int] NOT NULL ,
[PersonID] [int] NULL,
[StoreID] [int] NULL,
[TerritoryID] [int] NULL,
[AccountNumber] varchar(30),
[rowguid] [uniqueidentifier] ROWGUIDCOL NOT NULL,
[ModifiedDate] [datetime] NOT NULL)
GO
insert into [Customer] SELECT * FROM AdventureWorks2008.Sales.Customer
|
ALTER DATABASE TESTDB SET CHANGE_TRACKING = ON (CHANGE_RETENTION = 7 DAYS, AUTO_CLEANUP = ON);
|
USE TestDB
GO
ALTER TABLE customer enable CHANGE_TRACKING WITH (TRACK_COLUMNS_UPDATED = Off);
|
-- open a new session(1) and run the below statement
while 1=1
BEGIN
insert into [Customer] SELECT * FROM AdventureWorks2008.Sales.Customer
END;
-- open a 2nd new session(2) and run the below statement
while 1=1
BEGIN
update Customer set PersonID =customerid
END;
|
select XEventData.XEvent.value('(data/value)[1]', 'varchar(max)') as DeadlockGraph
FROM
(select CAST(target_data as xml) as TargetData
from sys.dm_xe_session_targets st
join sys.dm_xe_sessions s on s.address = st.event_session_address
where name = 'system_health' and target_name = 'ring_buffer') AS Data
CROSS APPLY TargetData.nodes ('//RingBufferTarget/event') AS XEventData (XEvent)
where XEventData.XEvent.value('@name', 'varchar(4000)') = 'xml_deadlock_report'
|
make sure before implementing change tracking on the tables with high volume of concurrent insert and updates. Change tracking creates few internal tables which are the main sources of causing these deadlocks.
During every modification on source table , it creates one record in the internal change tracking table. So , If Transaction A inserting records every 1 second and at the same time Transaction B is updating the records than the concurrent blocking will be placed on the Internal tables between these 2 transactions which leads to deadlocks.
Choose this option wisely or write your own custom code using other features where you can take full control.
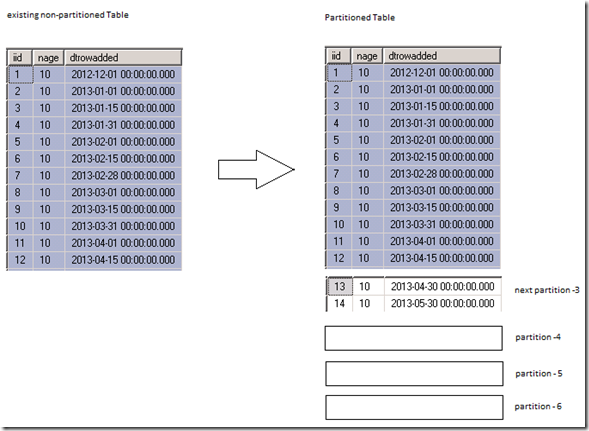
The major challenge involved in synchronizing the tables are identifying the modifications (updates) than the inserts/deletes as inserts/deletes can be identified by using an anchor table by comparing the primary keys in any data warehouse environment.



![clip_image002[1] clip_image002[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjH7USvF1-qL8wgcxZcMN2_0blrJuo6cwDcH7cJ0OgzXt5-bQ2qqlwephTptsBbBzZ7LIryN-LjH1UgW5yNZYBzPN9VXfP9j8kBh6Qo4D9xRz8hivI3g8Xc3nzGgYx9WevbZZqQgFq1PeCS/?imgmax=800)